How AI is Transforming Code Documentation: Experiments, Impacts, and New Perspectives
In recent months, I’ve experimented with various artificial intelligence tools dedicated to automatic code documentation generation. This is a rapidly evolving area with much deeper implications than it might seem: it’s not just about “writing better comments,” but about redefining how we understand, design, and maintain software, especially in a world where more and more code is generated through approaches like vibe coding or AI-assisted coding.
In this article, I share what I’ve observed: benefits, limitations, and new possibilities across three key areas:
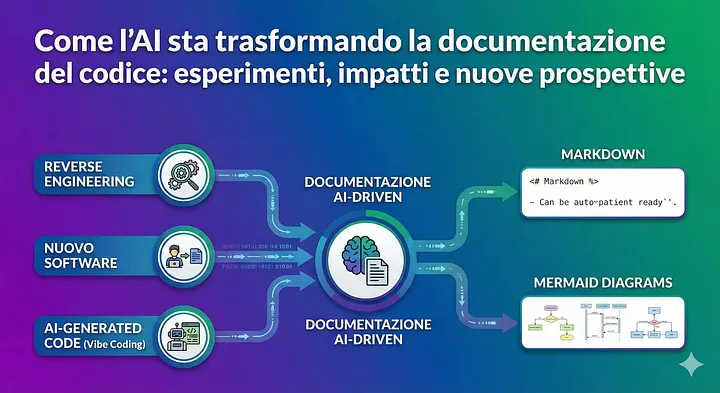
- Reverse engineering of existing systems
- Documentation of new software
- Documentation of AI-generated code (vibe coding)
And I’m adding a crucial aspect: the combined use of Markdown and Mermaid, which, together with AI, is revolutionizing technical documentation.
1. AI Documentation and Reverse Engineering: Understanding Complex Software Becomes More Accessible
Many legacy systems lack adequate documentation, or the documentation is outdated. AI tools today enable us to:
- Summarize entire codebases in minutes
- Generate architectural overviews
- Identify flows, dependencies, and side effects
- Explain complex functions and modules
- Reveal implicit patterns or anti-patterns
The result? A dramatic reduction in the time needed to understand code written by others, especially when there’s no documentation or when it’s scattered, inconsistent, or excessively technical.
2. Documentation for New Software: From Tedium to Continuous Workflow
With AI, documentation is no longer a burdensome afterthought. It becomes a natural part of the workflow:
- Documentation automatically generated at commit time
- Comments and descriptions produced in real-time
- Diagrams automatically updated when dependencies change
- READMEs and API guides created directly from the codebase
Documentation thus becomes synchronized, consistent, and finally maintainable.
3. Regaining Control Over AI-Generated Code (Vibe Coding)
When using vibe coding (prompt → AI generation → iteration):
- a lot of code is produced quickly
- not everything is read or verified in detail
- architecture can emerge “unintentionally”
- dependencies grow implicitly
Here, AI-generated documentation becomes fundamental to regaining control:
- it clarifies what was generated and why
- it explains algorithms and architectural choices
- it highlights critical points or fragile parts
- it makes transparent what would otherwise remain a “black box”
It’s a modern paradox: AI documents code written by AI, but it works.
🧩 4. Markdown + AI: The Perfect Pair for Technical Documentation
Markdown is the perfect format for AI-driven documentation:
- readable in text form
- completely versionable
- compatible with GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Medium, Notion
- ideal for READMEs, API guides, changelogs, technical SOPs
- extremely simple to generate automatically with AI
📄 Realistic example generated by AI from a real function:
### ⚙️ Function: processOrder(orderId)
**Description:**
Processes an order by retrieving data from the database, validating product availability, and updating the order status.
**Operational flow:**
1. Retrieve order data
2. Validate stock
3. Update DB
4. Notify user
**Dependencies:**
- `/services/inventory.js`
- `/services/notifications.js`
- `OrderRepository`This type of documentation can be produced automatically by analyzing the codebase.
🎨 5. Mermaid: Automatic Diagrams from Code (and Therefore Versionable)
Mermaid allows you to generate complex diagrams using simple text. AI can read the code and automatically produce:
- flowcharts
- sequence diagrams
- module dependencies
- ERD (Entity-Relationship Diagrams)
- microservice architectures
- system workflows
This makes a type of visual reverse engineering possible that has never been so accessible.
🔁 Example: Flowchart generated from the processOrder function
flowchart TD
A[Start] --> B[Retrieve order data]
B --> C{Stock available?}
C -- No --> D[Error: insufficient stock]
C -- Yes --> E[Update database]
E --> F[Send user notification]
F --> G[End]🧩 Example: module dependency map
graph LR
UI[UI Layer] --> API[API Gateway]
API --> SVC[Order Service]
API --> INV[Inventory Service]
SVC --> DB[(Order DB)]
INV --> DB2[(Inventory DB)]📡 Example: sequence diagram generated from code
sequenceDiagram
User->>UI: Place Order
UI->>API: POST /orders
API->>OrderService: createOrder()
OrderService->>InventoryService: checkStock()
InventoryService-->>OrderService: OK
OrderService->>DB: saveOrder()
DB-->>OrderService: saved
OrderService-->>API: orderId
API-->>UI: 200 OK🗄️ Example: ERD automatically generated from database schema
erDiagram
ORDERS ||--o{ ORDER_ITEMS : contains
PRODUCTS ||--o{ ORDER_ITEMS : referenced
ORDERS {
int id PK
datetime createdAt
string status
int userId
}
PRODUCTS {
int id PK
string name
float price
int stock
}
ORDER_ITEMS {
int id PK
int orderId FK
int productId FK
int quantity
float totalPrice
}🎯 6. Why This Combination is So Powerful
AI + Markdown + Mermaid enables:
- automatically generated and versionable documentation
- diagrams that are always up-to-date and reproducible
- visual flows consistent with the code
- immediate reverse engineering even on complex systems
- control over AI-generated code
In practice, we have for the first time an ecosystem of tools that:
- documents,
- visualizes,
- explains,
- versions,
- and evolves alongside the software.
Conclusion: Toward Human–AI Collaboration in Software Knowledge
Automatic documentation doesn’t replace human understanding: it amplifies it. The developer’s role is changing: from manual author of every line to curator of system knowledge.
We’re entering a new phase: documentation is becoming as intelligent as the software it describes.
And for the first time, we can document faster than we write code.